Allergy Vaccine Treatment
What is an allergy vaccine?
Allergy vaccine therapy (allergen immunotherapy) is the only treatment method that can change the course of the disease, prevent its progression, and even eliminate it completely when used in diseases such as allergic asthma and allergic rhinitis. It has been in use for more than 100 years. It is widely used in the treatment of allergic diseases in European countries and the USA.
Which patients are eligible for allergy vaccine treatment?
Allergy vaccine treatment can be administered to patients over 5 years of age. Patients with allergic asthma, allergic rhinitis, eye allergies, and bee venom allergies constitute the most eligible patient group for this treatment. In patients who are sensitive to to house dust, pollens, mold, cat dander and bee venom, there is good response to vaccine treatment.
What kinds of vaccines are available?
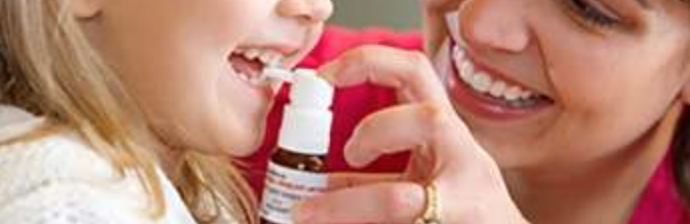
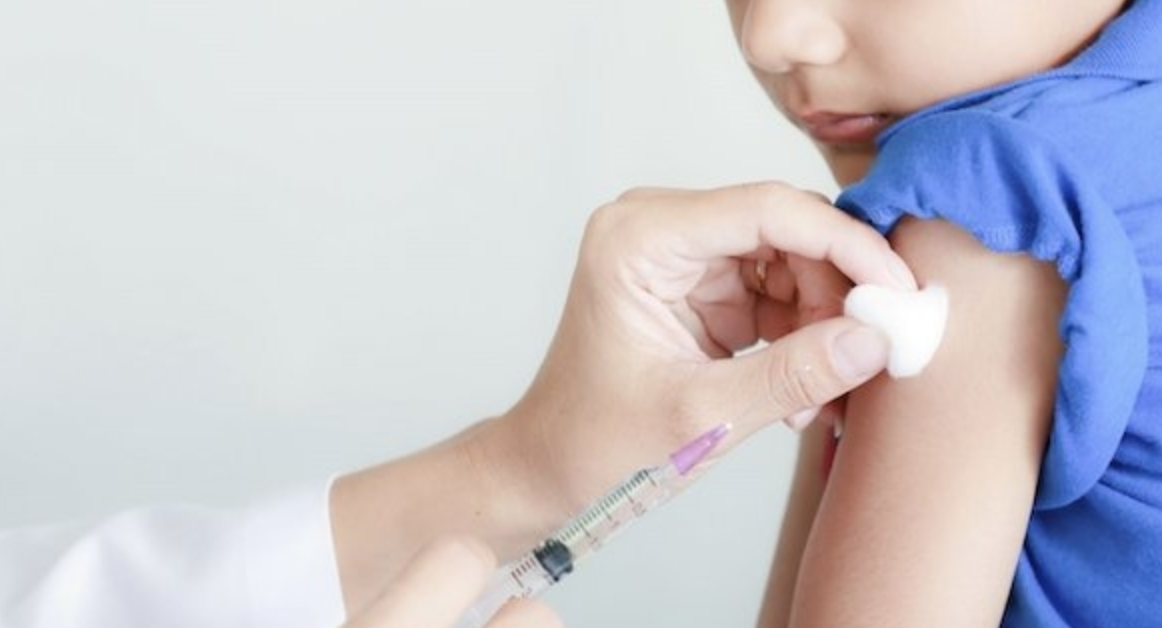
There are two forms: subcutaneous (administered under the skin by needle) and sublingual (administered under the tongue by mouth).
- Subcutaneous vaccine
- Sublingual vaccine
In subcutaneous administration, the efficacy is slightly higher with an earlier onset of action. However, this method should be used under the supervision of an allergy physician in conditions with the knowledge and equipment to intervene if an allergic reaction occurs, and 30 minutes of follow-up should be performed after the administration. In the sublingual method, subsequent doses can be given at home after the first dose is administered under the supervision of an allergist. Both methods are highly effective in the treatment of common allergic diseases such as childhood asthma and allergic rhinitis.
How long is allergy vaccine treatment used for?
It is recommended to use for an average of 4 years.
What is the administration scheme?
While sublingual vaccines preferably require daily administration, subcutaneous vaccines require weekly injections for the first few weeks, followed by monthly injections. It is important to complete the treatment for at least 4 years in order to achieve maximum efficacy.
What are the side effects?
- It is normal to have redness, itching, and swelling at the injection site after vaccination. In reactions with a diameter of 5 cm and above, the patient is kept under observation for a while, given local ice application and antihistamine medication.
- Although much rarer than local ones, side effects affecting the whole body may include rash, swelling of the tongue or lips, shortness of breath, hoarseness, tightness in the chest, runny nose, low blood pressure and rarely shock. In order to intervene in such situations, it is extremely important for patients to be under observation for 30 minutes after subcutaneous vaccination.
- In sublingual vaccines, temporary local side effects such as itching in the mouth and on the tongue, nausea, and vomiting are usually seen. As the vaccine treatment continues, most of them improve.
- Unlike drugs, the vaccine has no harmful side effects on internal organs. There is no drug or cortisone in vaccines, and they do not cause weight gain.
- They should be protected with the cold chain. They should be stored on the refrigerator shelf. They should be transported with ice batteries when going to the hospital or clinic. They should never be frozen.
How does the process progress after the treatment is completed and stopped?
It has been shown that the therapeutic effect of the vaccine treatment and preventing the progression of allergic diseases continues for many years.


